intermolecular forces
there are 3 types
van der walls which is the weakest ,dipole dipole, hydrogen bonding which is the strongest
van der walls
- they act between all molecules
- all atoms of molecules have positive and negative charges
- these charges will produce very weak electrostatic forces between the molecules and the atoms
- these electrostatic forces are called van der walls forces
- in any atom the electrons can be anywhere at any time , at an instant both electrons can be together at one time on one side this becomes slightly negative and is called a temporary dipole , because these electrons will keep moving and reoccurring
- the atom with the temporary dipoles will induce dipoles that are in near by atoms by attracting the positive nucleus
- this will be called instantaneous dipole and induced dipole forces
- the dipoles are caused by changing the position of the electron cloud
- the size of the van der walls forces increases as the size of the atom increases and the number of electrons available in the atom increases
- as the number of electrons increases the melting and boiling point increases , because more electrons are there which means there are more van der walls forces
common questions :
why is hexane a liquid at room temp and butane is a gas?
because the carbon chain is longer
dipole dipole forces
- only occur in molecules that have a polar bond
- in CO2 the dipoles cancel out
- dipole dipole are permanent and act between electronegative atoms
- the more the electronegative the atom is the stronger the electrostatic attraction will be which will make the atom pull electrons closer towards itself, this will lead to creating a delta negative side and a delta positive side
- molecules can attract similar molecules by filliping over to attract them so each side will be attracted to the opposite charge
molecules like H2 or O2 cant have dipole dipole forces because they are permanent and the atoms are the same
hydrogen bonding
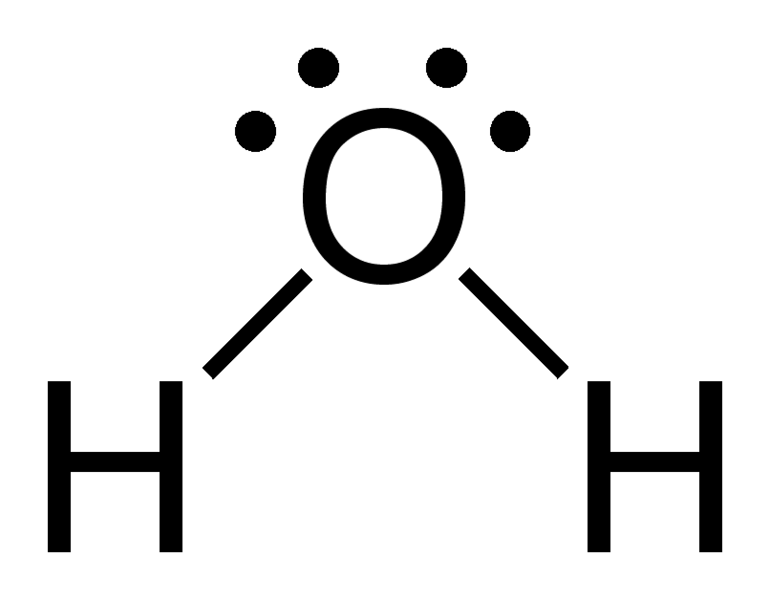
this is the strongest type of forces and it only occurs in FON - fluorine , oxygen and nitrogen covalently bonded to hydrogen
- hydrogen bonding only forms when one of the atoms is electronegative with a lone pair of electrons
- this is an example of the bonding in water where the oxygen is more electronegative that hydrogen and it has a lone par of electrons
- they are dipole dipole forces but they are much stronger due to having a lone pair and the hydrogen atoms are very small and very electron deficient , the protons are exposed. the lone pair of electrons on the electronegative oxygen on one water molecule is strongly attracted to the electron deficient hydrogen of another water molecule
TO FORM A HYDROGEN BOND WE NEED:- a hydrogen bonded to an electronegative atom so that the hydrogen has a partial charge
- an electronegative atom with a lone pair which will attract to the elctron deficient H forming a LINER BOND